Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a chronic infection of the tooth-supporting and surrounding structures. It is a leading cause of tooth loss in adults and is mostly brought about by improper oral hygiene. Periodontal disease, without regular oral care, can progress from mild inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) to aggressive periodontitis and ultimately to tooth and bone loss. Maintaining proper oral hygiene is vital so as not to develop periodontal disease. In this topic, we will discuss its cause, symptoms, classification, treatment, and prevention.
Understanding Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is a disease caused by infection that takes place as a result of the invasion of bacteria into the gums and the surrounding tissues. Periodontal disease is a disease of a progressive nature and begins with mild inflammation that gradually worsens with the progression of time unless treated.
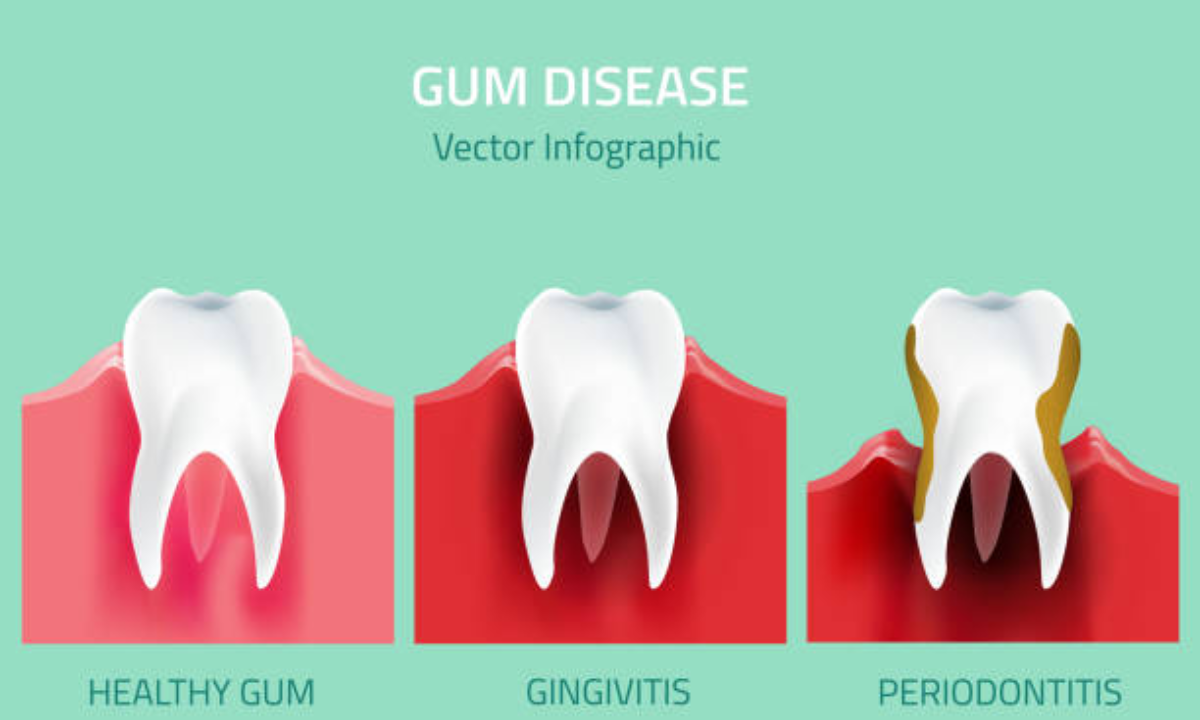
Gingivitis vs. Periodontitis
Gingivitis: This is the first stage of gum disease, and it is red, swollen gums that bleed. No long-term damage has been done to the bone or tissue yet.
Periodontitis: If gingivitis is not treated, it will later become periodontitis, where the infection is carried deeper into tissues, resulting in permanent loss of gums and bone.
Early detection and proper gum care will prevent mild gingivitis from progressing to advanced periodontitis.
Periodontal Disease Classification
Types of Periodontitis
- Chronic Periodontitis – The most common type, often in adults, with slow progression.
- Aggressive Periodontitis – Sudden loss of bone, usually in a young patient.
- Necrotizing Periodontal Disease – Tissue necrosis, usually associated with malnutrition or immunological disorder.
- Periodontitis as a Manifestation of Systemic Diseases – This can occur in conjunction with diseases like diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
Phases of Periodontal Disease
- Gingivitis – Mild gum inflammation with no loss of bone.
- Mild Periodontitis – Minor loss of bone with deepened gum pockets.
- Moderate Periodontitis – Increased gum recession with extensive bone loss.
- Severe Periodontitis – Advanced with widespread gum and bone loss with potential for losing teeth.
Know these so that they may be recognized early and treated accordingly.
Causes of Periodontal Disease
Role of Plaque Formation and Bacteria
The primary etiology of periodontal disease is plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that accumulates on teeth. Bacterial growth in plaque leads to gum infection and inflammation. Plaque that is not brushed and flossed away converts into tartar, leading to gum disease.
Other Factors Contributing
Several factors predispose individuals to the development of periodontitis, such as
- Poor oral hygiene – Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque buildup.
- Smoking and tobacco use – Delays healing and increases bacterial infection.
- Genetic predisposition – Individuals are more prone to gum disease due to genetic factors.
- Diabetes – Elevated blood sugar could increase gum disease risk.
- Hormonal changes – Pregnancy, menopause, and puberty can leave gums more vulnerable to infection.
By managing these risk factors, one can lower his or her risk of getting periodontal disease.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
- Early Gum Disease Symptoms
- Red, sore, or swollen gums
- Bleeding gums when brushing or flossing
- Bad breath (halitosis) that lingers
- Later Symptoms of Periodontitis
- Receding gums, elongating teeth
- Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums
- Loose or wiggly teeth
- Discharge of pus around teeth and gums
Early recognition of these symptoms and prompt dental treatment are necessary to prevent deterioration.
Diagnosis and Examination
Periodontal disease can be diagnosed by a dentist or periodontist through:
- Visual examination – Checking for signs of inflammation, gum recession, and bleeding.
- Periodontal probing – Assessment of the depth of gum pockets to gauge the severity of the disease.
- Dental X-rays – Identification of bone loss beneath teeth.
Regular dental checkup is held accountable for early diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Treatment of Gum Disease in Whitefield
The residents of Whitefield can approach specialized dentists to have their gum disease treatment at the top-class dental clinics in Whitefield.
Non-Surgical Procedure
- Dental professional cleaning – Bacteria and tartar removal.
- Scaling and root planing – Root deep scaling to remove the bacteria below the gum line.
- Antibiotic therapy –Represses the infection caused by the bacteria.
Surgical Procedure
- Flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery) – Eliminates gum pockets and cleans roots.
- Soft tissue grafts – These cover exposed roots and prevent gum recession.
- Bone grafting – This replaces lost bone to hold teeth.
Treatment of gum disease in Whitefield on time can avoid serious complications.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Gum Disease
- Dental Habits Daily
- Brushing teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to eliminate plaque between teeth.
- Antibacterial mouthwash to kill bacteria.
- Stop smoking – Prevents infection and supports healing.
- Eat well – Foods rich in nutrients keep gums healthy.
- Get regular dental checkups – Professional cleanings stop disease from advancing.
These habits can lower the risk of periodontal disease by a significant margin.
Choosing the Right Dental Clinic in Whitefield
While selecting a dental clinic in Whitefield, consider the following:
- Specialization in the treatment of periodontal – Ensure the clinic has specialists for advanced treatment.
- Use of contemporary technology – Contemporary technology can improve treatment results.
- Patient feedback and reviews – Good reviews guarantee quality service.
A visit to a quality dental clinic can help in the effective prevention and control of periodontal disease.
Conclusion
Periodontal disease is avoidable but can be serious. Good oral hygiene, management of risk factors, and professional care at a Whitefield dental clinic can assist people in protecting their gums and overall well-being. Treatment at the early stage is the best means of preventing serious complications, so act quickly. If you experience any gum disease symptoms, visit a dentist to get appropriate gum disease treatment in Whitefield so that you can smile with health.